India IVF Fertility presents an elucidative guide on the intricacies of pus cells in semen, delineating their relevance to fertility. This detailed exploration offers insights into the typical range of pus cells, underpins their significance, and elucidates potential interventions to mitigate their impact on reproductive health.
Decoding the Presence of Pus Cells
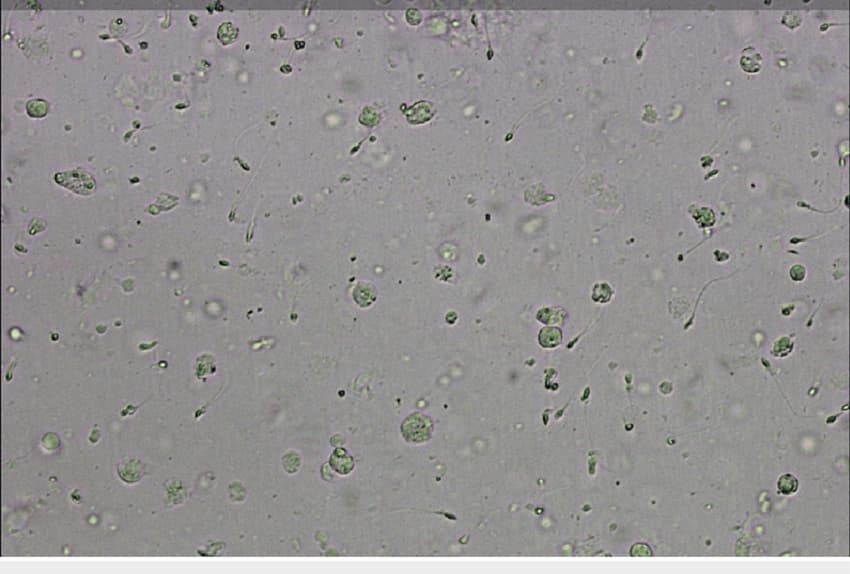
Pus cells, or leukocytes, within semen, are indicative of the immune system’s activity, chiefly deployed to combat infections. While their presence is nominal, an escalated count could signify underlying reproductive health concerns, meriting a closer examination of male fertility parameters.
Etiology Behind Increased Pus Cells
The proliferation of pus cells in semen can stem from various sources, including bacterial or viral afflictions in reproductive organs, sexually transmitted infections, or as a response to physical trauma or obstructions within the genital tract. Identifying the cause is pivotal for targeted treatment.
Symptomatology and Diagnostic Approach
Manifestations of elevated pus cells may include changes in semen color or odor, discomfort in the lower abdomen or genital region, and sometimes fever. Diagnosing this condition encompasses semen analysis, physical assessments, STI screening, and possibly ultrasound imaging to unearth any anatomical anomalies.
Therapeutic Interventions
Treatment modalities are contingent upon the underlying cause, ranging from antibiotics for bacterial infections to surgical remedies for anatomical impediments. Incorporating Ayurvedic principles for inflammation management represents an alternative or adjunct approach, emphasizing holistic well-being.
Fertility Outlook with Elevated Pus Cells
Pus cells per se do not directly impair fertility but the associated conditions—like infections or inflammations—could. These scenarios may affect sperm quality or lead to blockages in sperm transportation, thus impacting fertility.
Holistic Strategies for Reduction
Reducing pus cells naturally involves embracing a lifestyle conducive to reproductive health: staying hydrated, maintaining genital hygiene, practicing safe sex, consuming a balanced diet, engaging in regular physical activity, managing stress, securing ample sleep, and avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol consumption.
Comparative Analysis: Conventional vs. Ayurvedic Treatment for Pus Cells
| Treatment Method | Approach | Advantages | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Conventional | Antibiotics, anti-inflammatory drugs, surgery | Quick relief, targeted intervention | Potential side effects, resistance |
| Ayurvedic | Herbal remedies, lifestyle adjustments | Natural, holistic approach | Slower onset, efficacy varies |
Key Strategies for Maintaining Optimal Male Reproductive Health
- Routine Health Assessments: Regular check-ups with a healthcare professional to monitor reproductive health status;
- Balanced Nutrition: Incorporating a diet rich in antioxidants, vitamins, and minerals to support immune and reproductive system health;
- Adequate Hydration: Drinking plenty of water daily to aid in the removal of toxins from the body and maintain semen quality;
- Physical Activity: Engaging in regular exercise to improve circulation, reduce stress, and enhance overall well-being;
- Stress Management: Utilizing techniques such as meditation, yoga, or deep breathing exercises to manage stress levels effectively;
- Safe Sexual Practices: Employing protective measures to prevent sexually transmitted infections that can lead to increased pus cells;
- Avoidance of Harmful Substances: Limiting intake of alcohol, quitting smoking, and avoiding recreational drugs to protect reproductive health;
- Proper Genital Hygiene: Maintaining cleanliness to prevent infections that could increase pus cell counts in semen;
- Adequate Rest and Sleep: Ensuring sufficient sleep to support the body’s natural repair processes, including those affecting reproductive health;
- Consultation with Specialists: Seeking guidance from fertility specialists or urologists for personalized advice and advanced treatments if necessary.
Incorporating these strategies into daily life can significantly contribute to the maintenance of male reproductive health, potentially reducing the occurrence of issues such as elevated pus cells in semen.
Understanding the Immune System’s Role in Reproductive Health
The immune system plays a pivotal role in maintaining the body’s overall health, including the reproductive system. In the context of male fertility, the presence of pus cells, or leukocytes, in semen is a manifestation of the immune system’s response to potential threats such as infections or injuries within the reproductive tract. Normally, a few these cells are present as part of the body’s natural defense mechanism. However, an elevated count can indicate an ongoing issue that may need further investigation.
The balance between protecting the body and maintaining fertility is delicate. While leukocytes defend against infections, their excessive presence can create an environment that is hostile to sperm, potentially impacting sperm function and motility. Understanding how the immune system interacts with the reproductive system is crucial for diagnosing and treating conditions that could impair fertility. It involves a comprehensive approach that considers both the protective measures of the immune response and the need to preserve or enhance reproductive capabilities. Advances in medical research continue to shed light on this complex interplay, offering new insights into treatments that can support both immune and reproductive health without compromising one for the other.
The Impact of Lifestyle on Semen Quality and Fertility
Lifestyle choices have a significant impact on semen quality and, by extension, male fertility. Factors such as diet, exercise, stress levels, and substance use all play critical roles in determining the health of sperm and semen. For instance, diets rich in antioxidants can protect sperm from oxidative stress, enhancing their viability and motility. Similarly, regular physical activity has been linked to improvements in sperm count and morphology, though excessive or intense exercise without adequate rest can have the opposite effect.
Stress management is another critical component. Chronic stress can lead to hormonal imbalances that affect sperm production. Techniques for stress reduction, such as mindfulness, yoga, or regular physical activity, can improve semen quality by restoring hormonal balance and reducing oxidative stress within the body.
Substance use, including smoking tobacco, consuming excessive alcohol, and using recreational drugs, can negatively affect sperm DNA, reducing fertility. Quitting smoking and moderating alcohol intake are beneficial steps toward improving reproductive health.
Adopting a lifestyle that supports overall well-being can have profound effects on semen quality and fertility. It’s about making informed choices that not only enhance personal health but also the potential for successful conception. The relationship between lifestyle and fertility is a reminder of the body’s interconnectedness, where positive changes in one area can lead to improvements in another, ultimately supporting the goal of achieving and maintaining optimal reproductive health.
Conclusion
Understanding the dynamics of pus cells in semen is crucial for addressing male fertility concerns effectively. While pus cells are a single facet of a comprehensive fertility assessment, they underscore the importance of a holistic approach to reproductive health. Consulting healthcare professionals for personalized advice and adopting a health-oriented lifestyle are fundamental steps toward optimizing fertility prospects.