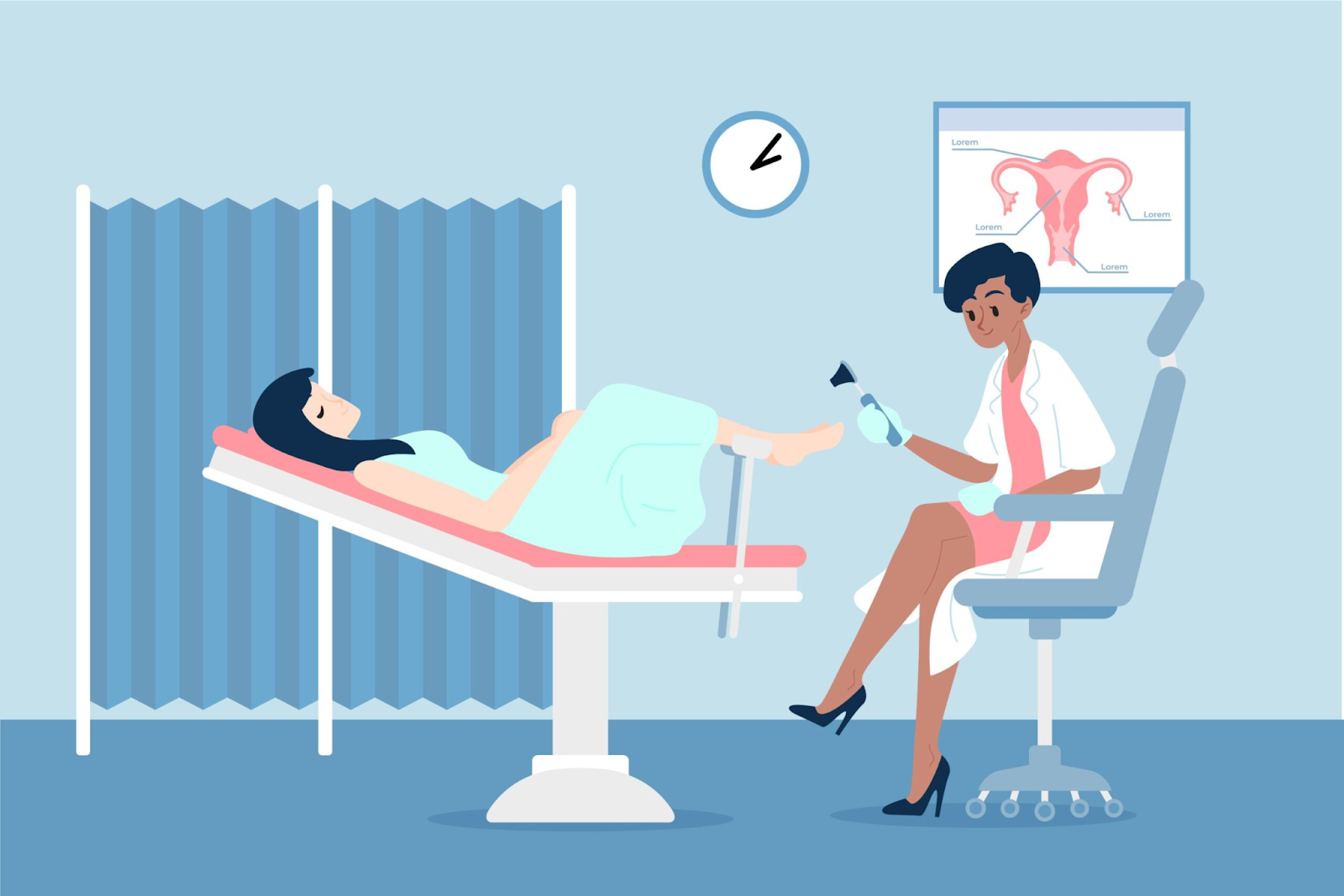
Artificial insemination (AI) is a widely used method in modern cattle breeding to improve herd genetic potential and productivity. Here are some of the AI methods that are used in cattle and their comparative performance analysis.
Direct injection of semen (rectal insemination)
Process: Semen is injected directly into the cow’s uterus through rectal insertion using a special apparatus.
Advantages: Relatively simple process requiring little equipment.
Disadvantages: Not always effective due to possible injury and infection during semen insertion.
Intracervical injection
Process: Semen is injected into the cow’s cervix using a special syringe and catheter.
Advantages: More accurate injection of semen, which can improve the chances of pregnancy.
Disadvantages: Requires skill and experience to perform the procedure, as well as additional equipment.
Intrauterine injection
Process: Semen is injected directly inside the cow’s uterus using a special catheter.
Advantages: May be more effective than other methods because the semen is injected closer to the site of fertilization.
Disadvantages: Requires a highly skilled operator and additional equipment costs.
Intravaginal injection
Process: Semen is injected into the cow’s vagina using a special catheter.
Advantages: Relatively simple and affordable procedure.
Disadvantages: May be less effective than other methods due to possible loss of semen during insertion.
Comparative analysis of effectiveness
Each of these methods has advantages and disadvantages, and effectiveness depends on many factors, including operator skill, cow health, semen quality, and others. Conducting a comparative analysis will help in selecting the most appropriate method that will maximize efficiency and productivity of the cattle herd.