The phenomenon of insipid secretions, or the thickening of bodily fluids, emerges as a critical health concern, characterized by an increase in fluid viscosity within body channels or cavities. Such conditions are primarily seen in the nasal passages, sinuses, oral cavity, or various ducts, commonly resulting from dehydration—a process that often becomes chronic. The progressive thickening of these secretions can obstruct the natural flow in airways or ducts, with some instances leading to calcification, known as dystrophic calcification. This overview aims to dissect the origins, health impacts, and management strategies of thickened bodily fluids, offering a comprehensive understanding for healthcare professionals and caregivers.
Clinical Implications and Biological Significance
Individuals suffering from certain chronic conditions may experience dehydration, which in turn precipitates the formation of dense, sticky secretions composed of cellular waste. This phenomenon can obstruct airways or ducts, posing potentially severe health risks. Conditions such as asthma, allergies compounded by superinfections, cystic fibrosis, effects of intubated ventilation, injuries from burns, and side effects from certain medications are central to discussions within this context. Importantly, patients with severe chronic conditions may be non-verbal, and unable to alert caregivers to airway blockages or obstructions. Hence, it’s crucial to ensure adequate hydration and maintain meticulous oral hygiene, not just for dental care but also for the mucosal surfaces within the mouth.
Special attention is warranted for individuals who are bedridden or in institutional care to avert negative outcomes. Implementing daily oral care routines, such as cleansing with a chlorhexidine-dampened surgical sponge, can significantly reduce the risk of aspiration pneumonia or fatalities from airway blockages. Oral and nasal secretions play vital roles in immunity, digestion, lubrication, and speech, with saliva being particularly significant due to its volume. These secretions aid in moisturizing the air breathed in and out but can become highly viscous upon dehydration, trapping particles, food residue, and bacteria, thus exacerbating insipidation and potential airway obstruction.
Prevention and Management
To prevent the severe consequences of insipid secretions, it is imperative to focus on hydration and comprehensive oral hygiene. These measures not only aid in reducing the viscosity of bodily secretions but also minimize the risk of obstruction in airways and ducts. Regular monitoring and proactive care are especially crucial for at-risk populations, including those with chronic conditions, the elderly, and individuals under long-term care.
Impact on Health and Wellness
Thickened secretions pose a significant health risk by obstructing crucial pathways in the human body, such as airways and ducts. This obstruction is particularly hazardous for individuals with chronic conditions like asthma, cystic fibrosis, or those suffering from burn injuries. These blockages can exacerbate existing health issues, leading to severe complications or even life-threatening situations. Furthermore, the calcification of these secretions adds another layer of complexity, potentially leading to further health deterioration. Understanding these impacts is vital for developing effective management and prevention strategies.
Strategies for Effective Management
Managing insipid secretions involves a multifaceted approach focusing on hydration, oral hygiene, and monitoring for at-risk individuals. Hydration plays a pivotal role in reducing secretion viscosity, thereby minimizing the risk of obstruction. Oral hygiene, particularly for individuals who are non-verbal or bedridden, requires meticulous attention to prevent the accumulation of secretions that could lead to blockages. Routine oral care, including the use of antiseptic solutions, can significantly mitigate the risks associated with thickened bodily fluids.
Unique Prevention Techniques
Preventing the adverse effects of thickened bodily fluids involves several proactive measures:
- Regular Hydration: Encourage frequent fluid intake to maintain optimal hydration levels, preventing the secretions from thickening;
- Comprehensive Oral Hygiene: Implement daily routines focusing on the entire oral cavity, not just the teeth, to reduce the risk of secretion accumulation;
- Close Monitoring: Pay special attention to individuals with chronic conditions or those in long-term care, as they are at higher risk for developing complications from thickened secretions.
Innovative Approaches to Diagnosing Thickened Secretions
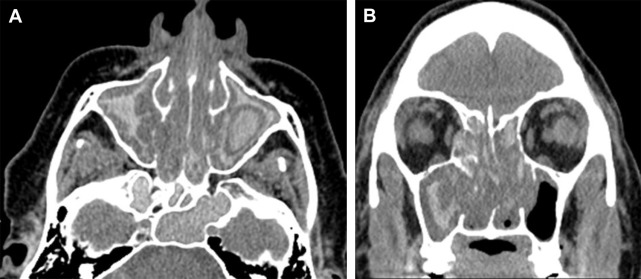
In the realm of medical science, the early diagnosis of thickened secretions is pivotal for effective treatment and prevention of further complications. Emerging technologies and methodologies offer new avenues for detecting these conditions with greater accuracy and speed. One such innovation is the use of high-resolution imaging techniques, such as MRI and CT scans, which can provide detailed views of bodily ducts and cavities, revealing the presence and extent of thickened secretions. Additionally, advancements in biochemical analysis now allow for the detailed examination of the composition of bodily fluids, identifying changes in viscosity and the potential for obstruction more precisely.
These diagnostic tools not only facilitate a deeper understanding of the condition but also enable personalized treatment plans tailored to the specific needs and circumstances of each patient. The integration of these innovative diagnostic approaches represents a significant leap forward in the management of diseases associated with thickened bodily fluids, offering hope for improved outcomes and quality of life for affected individuals.
The Role of Diet and Nutrition in Managing Thickened Secretions
Diet and nutrition play a crucial role in the management and prevention of thickened bodily secretions. Adequate hydration is the cornerstone of preventing the thickening of secretions, but the composition of one’s diet can also have a profound impact. A balanced intake of electrolytes, particularly potassium and sodium, helps regulate body fluids’ balance, supporting optimal hydration levels. Additionally, incorporating foods with high water content, such as fruits and vegetables, can further aid in maintaining hydration.
Omega-3 fatty acids, found in fish and flaxseeds, have been shown to have anti-inflammatory properties, which may be beneficial in reducing the risk of ductal or airway inflammation leading to secretion thickening. Moreover, reducing the intake of foods that can contribute to dehydration, such as those high in sugar or caffeine, is also advisable. Tailoring dietary habits to support hydration and reduce inflammation can be a valuable component of a comprehensive approach to managing thickened secretions, complementing medical treatments and enhancing overall health outcomes.
Key Takeaways
- Thickened bodily fluids, or insipid secretions, are primarily caused by dehydration and can obstruct critical body pathways;
- Conditions such as cystic fibrosis, asthma, and others significantly increase the risk of complications from thickened secretions;
- Effective management includes maintaining hydration, ensuring meticulous oral hygiene, and routine monitoring of at-risk individuals;
- Proactive prevention strategies are crucial for mitigating the risks associated with thickened bodily fluids, emphasizing the importance of regular hydration and comprehensive oral care;
- Understanding the implications and management strategies for thickened bodily fluids is essential for healthcare professionals and caregivers, enabling them to provide better care for individuals at risk.
Conclusion
The thickening of bodily secretions due to dehydration presents a significant health challenge, particularly in individuals with chronic diseases or conditions that impair their ability to communicate discomfort or distress. Understanding the clinical, biological, and physiological importance of these secretions underscores the necessity of proactive management strategies focused on hydration and oral hygiene to mitigate risks associated with insipid secretions.