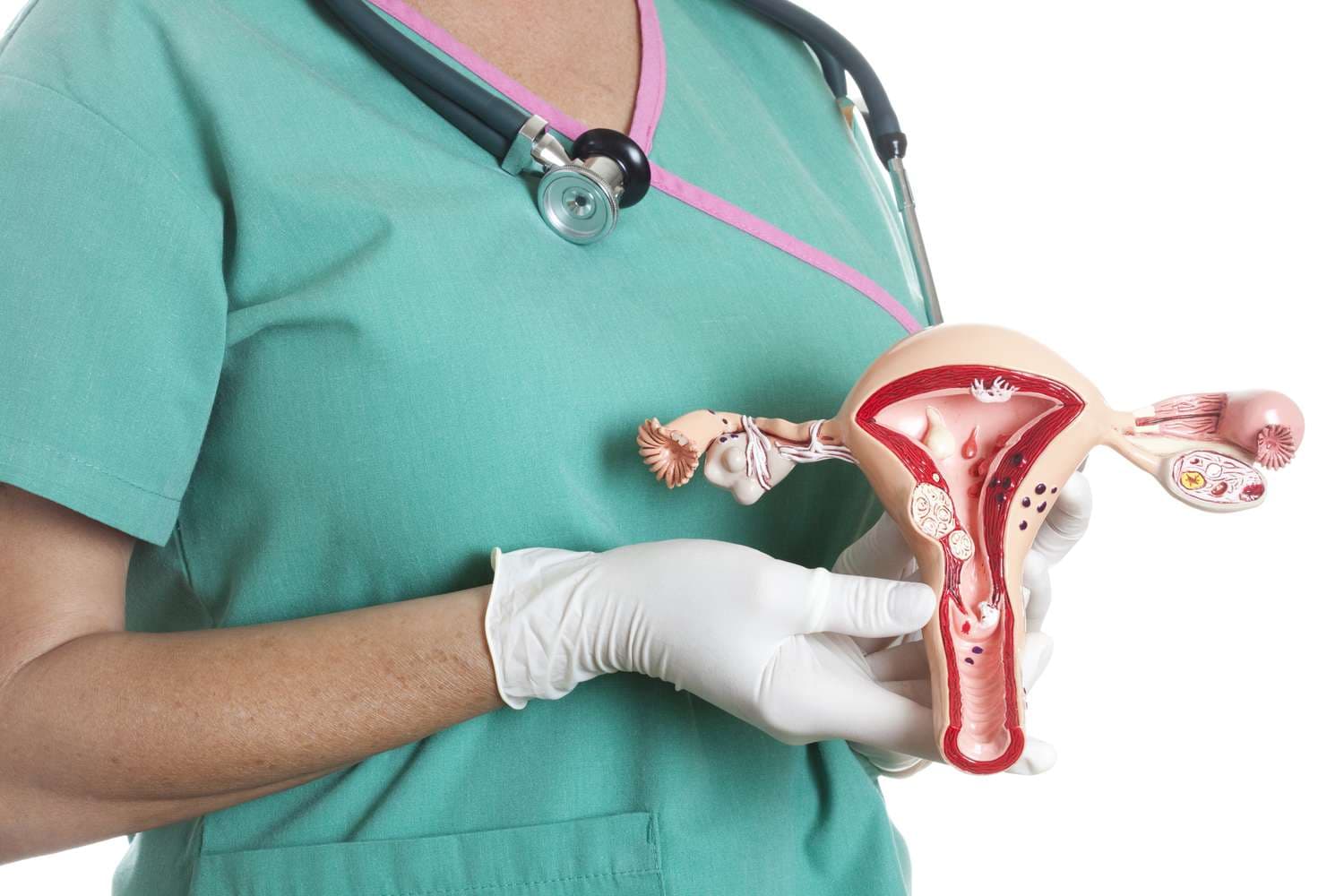
The ovarian bursa, a pivotal structure within the mammalian female reproductive system, encompasses the ovary, facilitating crucial processes such as ovulation and the initial stages of gamete transport. Its strategic positioning and structure reflect an evolutionary design optimized for reproductive efficiency and protection of the gametes from external threats.
Structural Details of the Ovarian Bursa
Comprising a delicate membrane, the ovarian bursa encapsulates the ovary, forming a protective sac. This enclosure is not merely a physical barrier but a dynamic environment conducive to the ovary’s functional demands. The layers of the bursa, intricately designed, permit selective transfer of substances, ensuring the ovary’s physiological needs are met while maintaining a controlled internal milieu.
Functional Importance of the Ovarian Bursa
The ovarian bursa’s role transcends mere protection, extending to the facilitation of effective ovulation and gamete transport. By enveloping the ovary, it creates a specialized site where ovulation can occur with minimal disturbance, ensuring the direct capture of the oocyte by the fallopian tubes. Furthermore, it serves as a first line of defense against infections, highlighting its significance in reproductive health and disease prevention.
Comparative Anatomy: Ovarian Bursa Across Species
A comparative anatomical study reveals variations in the ovarian bursa’s structure and function across different mammalian species, reflecting adaptations to diverse reproductive strategies. These differences offer insights into the evolutionary pressures shaping reproductive anatomy and provide valuable perspectives for both biological research and veterinary practices.
Key Features of the Ovarian Bursa
- Anatomical Position: Encloses the ovary, situating it within a protective sac that is integral to the female reproductive system;
- Structural Composition: Comprised of the mesovarium, which connects the ovary to the broad ligament, encapsulating the ovary in a supportive framework;
- Functionality: Facilitates the direct transfer of oocytes from the ovary to the fallopian tubes, playing a crucial role in the reproductive process;
- Protective Role: Shields the ovary from external physical damage and potential infections, maintaining the integrity of the female reproductive organs;
- Vascular Supply: Richly supplied with blood vessels, ensuring the ovary receives necessary nutrients and hormonal signals for its functions;
- Endocrine Interaction: The proximity within the bursa allows for efficient hormonal communication between the ovary and the rest of the reproductive system;
- Clinical Significance: Understanding its structure and function is vital for diagnosing and treating various reproductive disorders effectively.
Evolutionary Perspectives on the Ovarian Bursa
The ovarian bursa, a pivotal structure within the female reproductive system, showcases a remarkable example of evolutionary refinement. This sac-like cavity, encapsulating the ovary, has evolved to optimize reproductive efficiency and protection. In mammals, the ovarian bursa forms a direct conduit for oocytes from the ovary to the fallopian tubes, minimizing the distance they must travel to be fertilized. This adaptation significantly increases the chances of successful fertilization and subsequent embryo development. Moreover, the protective environment of the bursa guards against external physical impacts and microbial invasion, which could compromise ovarian health and fertility.
The evolutionary development of the ovarian bursa underscores the intricate balance between structural protection and functional efficiency in reproductive anatomy. By fostering a controlled environment for oocyte maturation and release, the bursa exemplifies how evolutionary pressures shape anatomical structures to enhance species survival through successful reproduction.
Clinical Implications and Future Directions
The ovarian bursa’s role transcends its basic anatomical functions, extending into various clinical implications. Understanding its structure and function is crucial for the early detection and treatment of reproductive pathologies such as ovarian cysts, ectopic pregnancies, and inflammatory diseases. For instance, conditions that compromise the integrity of the bursa can lead to impaired fertility, highlighting the need for precise diagnostic and surgical techniques in gynecology. Moreover, advancements in reproductive technology and surgery continue to benefit from a deep understanding of the bursa’s anatomy. Laparoscopic procedures, for instance, require meticulous navigation of the bursa to access the ovaries for treatments like cyst removal or ovary harvesting for assisted reproductive technologies.
Looking ahead, research into the molecular and cellular mechanisms governing the ovarian bursa could unveil new therapeutic targets for fertility enhancement and the treatment of reproductive disorders. Additionally, the study of bursa’s evolutionary variations across different species may offer insights into alternative reproductive strategies and potential applications in veterinary medicine and conservation biology. The ovarian bursa, therefore, not only plays a foundational role in female reproductive health but also represents a focal point for future clinical and research advancements.
Conclusion
Understanding the ovarian bursa’s anatomy and function sheds light on its critical role in mammalian reproduction. Future research directions may focus on elucidating the bursa’s involvement in reproductive disorders and its potential as a target for therapeutic interventions. As our knowledge expands, so too will our ability to address reproductive health issues with greater precision and effectiveness.