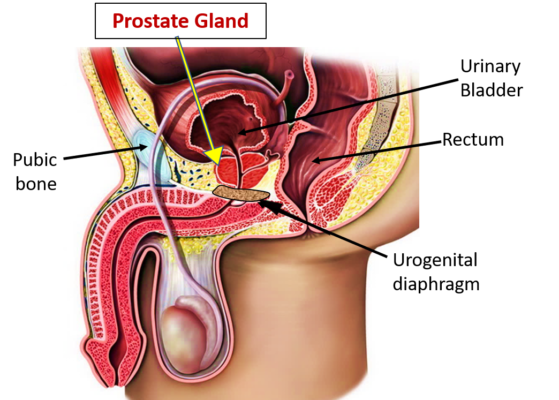
The colliculus seminalis, also known as verumontanum, is a crucial anatomical feature situated in the prostatic urethra, serving as a key landmark near the entry point of the ejaculatory ducts. This median elevation, likened to a ‘mountain ridge,’ plays a pivotal role in the urethral anatomy and function, particularly in the context of male reproductive health.
Anatomical Position and Structure
Located within the prostatic urethra, the colliculus seminalis is distinguished by its median protrusion and serves as the juncture for the ejaculatory ducts. This feature is essential for the proper passage of semen, with adjacent structures including the prostatic utricle and openings of the prostatic ducts contributing to its functional and anatomical significance.
Embryological Origins and Importance
Emerging from the uterovaginal primordium, the colliculus seminalis is integral to the development of the urethra and is involved in various urethral developmental disorders. Its embryological development underscores its role in the classification and understanding of these conditions, emphasizing its importance beyond mere anatomy.
Associated Urethral Disorders
The verumontanum’s position and structure are vital in diagnosing and managing posterior urethral valves, a congenital anomaly leading to urethral obstruction in newborn males. Additionally, it’s a site where urethral carcinoid tumors may develop, and its displacement is observed in hypospadias, illustrating its clinical relevance in urological pathologies.
Examination and Clinical Significance
Clinical examination of the colliculus seminalis, through methods such as endoscopy, is crucial for diagnosing various conditions, including seminal vesiculitis and urethral obstructions. Its visibility during such procedures provides valuable insights into the health of the male reproductive tract, highlighting its significance in both diagnostic and therapeutic contexts.
Features of the Seminal Colliculus
- Central Role in Ejaculation: Acts as a critical pathway for semen ejection;
- Embryological Significance: Originates from the uterovaginal primordium, indicating its developmental importance;
- Anatomical Landmark: Serves as a key point of reference in the prostatic urethra for medical examinations and surgical interventions.
Comparative Analysis: Seminal Colliculus vs. Other Urethral Structures
| Feature | Seminal Colliculus | Prostatic Utricle | Ejaculatory Ducts |
|---|---|---|---|
| Location | Within the prostatic urethra | Adjacent to the seminal colliculus | Originating from the seminal vesicle |
| Function | Passage for semen during ejaculation | Vestigial structure, no direct function | Transport semen to the urethra |
| Clinical Significance | Key in diagnosing urethral disorders | Associated with hypospadias | Involved in ejaculatory dysfunction |
| Visibility in Procedures | Prominently visible during endoscopy | May be visible in a detailed examination | Rarely seen directly in procedures |
The Role in Reproductive Health
The seminal colliculus’s strategic positioning within the male reproductive system underscores its role in facilitating successful ejaculation. By serving as the confluence point for the ejaculatory ducts, it ensures the efficient passage of semen, integrating contributions from the seminal vesicles and vas deferens. This efficiency is paramount for reproductive success, making the colliculus seminalis a focal point in studies related to male fertility and sexual health.
Impact on Urological Disorders
Given its crucial anatomical placement, the seminal colliculus is often at the heart of several urological disorders, including posterior urethral valves and ejaculatory duct obstructions. Its involvement in these conditions can lead to significant complications, ranging from urinary retention to infertility. Understanding its role allows for targeted therapeutic interventions, highlighting its importance beyond mere anatomical interest.
Examination Techniques
Innovative diagnostic techniques have revolutionized the examination of the seminal colliculus, making it more accessible and easier to evaluate. Endoscopic procedures, specifically designed for deep urethral inspection, offer a high-definition view of this structure, enabling precise identification of anomalies. Such advancements not only facilitate early diagnosis but also aid in the precise delivery of treatments, underscoring the seminal colliculus’s significance in urological care.
Conclusion
The colliculus seminalis is more than just a landmark within the prostatic urethra; it is a vital component in understanding male urethral anatomy, embryology, and associated pathologies. Its examination and the knowledge of its structural and functional aspects are essential for healthcare professionals in diagnosing and treating related disorders effectively.